ตำรามาตรฐานยาสมุนไพรไทย
Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia
สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข
Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health(Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook.f. & Thomson)
(Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.)
(Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.)
(Centella Dry Extract)
(Centella Cream)
(Mesua ferrea L.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Pterocarpus santalinus L. f.)
(Santalum album L.)
(Senna tora (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna alata (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna Alata Tea)
(Piper retrofractum Vahl)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees)
(Andrographis Capsules)
(Allium ascalonicum L.)
(Ocimum tenuiflorum L.)
(Curcuma longa L.)
(Turmeric Capsules)
(Turmeric Dry Extract)
(Turmeric Dry Extract Capsules)
(Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.)
(Curcuma sp.)
Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.
(Aristolochia pierrei Lecomte)
(Zingiber officinale Roscoe)
(Ginger Capsules)
(Ginger Tea)
(Cassia fistula L.)
(Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC.)
(Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels)
Artemisia annua L.
(Ligusticum sinense Oliv. cv. Chuanxiong)
(Neopicrorhiza scrophulariiflora Pennell)
(Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC.)
(Aucklandia lappa Decne)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Angelica dahurica (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook. f. ex Franch. & Sav. var. dahurica)
(Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker)
(Hibiscus sabdariffa L.)
(Roselle Tea)
(Allium sativum L.)
(Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Sm.)
(Wurfbainia testacea (Ridl.) Škorničk.& A. D. Poulsen)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S. C. Chen)
(Ficus racemosa L.)
(Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit.)
Clerodendrum indicum (L.) Kuntze
(Phyllanthus emblica L.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Areca catechu L.)
(Momordica charantia L.)
Moringa oleifera Lam.
(Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa)
(Solanum trilobatum L.)
(Morus alba L.)
Gynostemma pentaphyllum(Thunb.)
Makino
(Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau)
(Cissus quadrangularis L.)
(Mimusops elengi L.)
(Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link. ex A. Dietr.)
(Piper betle L.)
(Capsicum annuum L.)
(Capsicum Oleoresin)
(Capsicum Gel)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Eurycoma longifolia Jack)
(Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl.)
(Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz.)
Senna garrettiana (Craib) H. S. Irwin & Barneby
(Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb.)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) H. Roxb.)
(Tarlmounia elliptica (DC.) H. Rob., S. C. Keeley, Skvaria & R. Chan)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract Capsiles)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract)
(Brachypterum scandens (Roxb.) Miq.)
(Lepidium sativum L.)
(Nigella sativa L.)
(Cuminum cyminum L.)
(Foeniculum vulgare Mill.)
(Plantago ovata Forssk.)
(Pimpinella anisum L.)
(Carum carvi L.)
(Anethum graveolens L.)
(Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague)
Albizia procera (Roxb.) Benth.
(Acorus calamus L.)
(Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels)
Cyanthillium cinereum (L.) H. Rob.
(Orthosiphon aristatus (Blume) Miq.)
Murdannia loriformis (Hassk.) R. S. Rao & Kammathy
(Capparis micracantha DC.)
(Chrysopogon zizanioides (L.) Roberty)
(Cyperus rotundus L.)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. & L. M. Perry)
(Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf.)
(Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl)
(Acanthus ilicifolius L.)
(Kaempferia galanga L.)
(Curcuma comosa Roxb.)
Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don
Cannabis sativa L.
Carthamus tinctorius L
Mitragyna speciosa (Korth.) Havil
Mallotus repandus (Rottler) Müll. Arg
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
Baliospermum solanifolium (Burm.) Suresh
Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb
Boesenbergia kingii Mood & L. M. Prince
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senna alexandriana Mill. var. alexandriana
Cassia acutifolia Delile, Cassia angustifolia Vahl
Butea superba Roxb. ex Willd.
[Plaso superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Kuntze, Rudolphia superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Poir.
Pueraria candollei Graham
ex Benth. var. mirifica (Airy Shaw & Suvat.) Niyomdham
Streblus asper Lour.
Suregada multiflora (A. Juss.) Baill. (Gelonium
multiflorum A. Juss.
Plumbago zeylanica L.
Plumbago indica L.
Biancaea sappan (L.) Tod.
Ziziphus attopensis Pierre
Streblus asper Lour.
Justicia gendarussa Burm. f.
Enhalus acoroides (L. f.) Royle
Bridelia ovata Decne.
Tamarindus indica L.
Citrus × aurantiifolia (Christm.) Swingle
Garcinia mangostana L.
Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC
Persicaria odorata (Lour.) Soják
Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link ex A. Dietr.
Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anderson
Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr.
Citrus × aurantium L. ‘Som Sa’
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
Himalayan Birch Bark is the dried stem bark of Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don [B. affinis (Spach) Endl., B. nitida D. Don] (Family Betulaceae), Herbarium Specimen Number: DMSC 5332, Crude Drug Number: DMSc 1226.
Constituents Himalayan Birch Bark contains triterpenoids (e.g., betulin, betulinic acid, lupeol, oleanolic acid, and ursolic acid). It also contains phenolics such as methyl salicylate and arbutin.
Description of the plant (Fig. 1) Tree up to 35 m tall, monoecious; bark red-brown or silvery grey, with large oblong lenticels, exfoliating into thin slices; inner bark strongly aromatic; branchlet densely white villous, with resinous glands. Leaves simple, spirally arranged, ovate-lanceolate, ovate-elliptic, to ovate-oblong, 4 to 14 cm long, 2.5 to 5.5 cm wide, apex acuminate or caudate-acuminate, base cuneate to broadly cuneate or subrounded, rarely subcordate, margin serrate, papery, abaxially densely glandular punctate, sparsely villous along veins, bearded in axils of lateral veins, adaxially glabrous, lateral veins 8 to 13 on each side of midvein; petiole 1.5 to 4 cm long, densely white villous, with resinous glands. Inflorescence terminal or axillary pendulous catkins, cylindrical; pedunculate. Flower tiny, greenish, perianth minute. Staminate inflorescence up to 20 cm long, about 4 mm wide; bracts numerous, overlapping, each bract subtending 2 bracteoles and 3 flowers; staminate flowers: stamens 2, anthers 2-loculed, thecae connate, apex pubescent or glabrous. Pistillate inflorescence 5 to 10 cm long, 4 to 6 mm wide, in group of 2 to 5; peduncle 2 to 3 mm long, densely yellow villous; bract about 3 mm long, densely pubescent and ciliolate, becoming spongy at base, 3-lobed, middle lobe oblong or obtuse, lateral lobes reduced, auriculate, each bract subtending 3 ovaries at base; pistillate flowers: ovary, 2-loculed, each locule with 2 ovules, styles 2, persistent. Fruit a nutlet, with membranous wings; nutlet obovate, about 4 mm long (wings included), apex sparsely pubescent, flattened, with membranous wings twice as wide as nutlet.
Description Odour, slightly methyl salicylate-like; taste, slightly pungent.
Macroscopical (Fig. 1) Curved stem bark, 1.0 to 3.5 cm thick. Outer surface whitish brown to reddish brown, slightly rough, with parts of exfoliated yellowish brown of remained periderm, phellem slightly with scattered long horizontal whitish shallow groove of lenticels. Inner surface smooth, reddish brown.
Microscopical (Figs. 2a, 2b) Transverse section of the stem bark shows outer bark and inner bark. Outer bark: several layers of cork, some containing brown or red substance and groups of sclereids, some containing brown or red substance. Inner bark: groups of sclereids, phloem ray, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma, some containing starch grains, prismatic crystals, rosette aggregate crystals or brown substance.
Himalayan Birch Bark in powder possesses the diagnostic microscopical character of the unground drug. Groups of thick-walled sclereids with brown or red substance and thick-walled parenchyma containing brown substance are characteristic.




Packaging and storage Himalayan Birch Bark shall be kept in well-closed containers, protected from light, and stored in a cool and dry place.
Identification
A. To 1 g of the sample, in No. 250 powder, add 30 mL of water and heat on a water-bath for 20 minutes. Immediately filter through a plug of cotton wool and allow the filtrate to cool. Shake 5 mL of the filtrate with 2 mL of chloroform for 2 minutes. Separate the chloroform layer and transfer 1 mL of this layer to a test-tube, slowly add a few drops of sulfuric acid to form a layer: a reddish brown ring forms at the zone of contact.
B. Boil 1 g of the sample, in No. 250 powder, with 20 mL of water, cool and filter. To 1 mL of the filtrate, add 5 mL of water, mix and then add a few drops of iron(III) chloride TS: a dark blue precipitate develops.
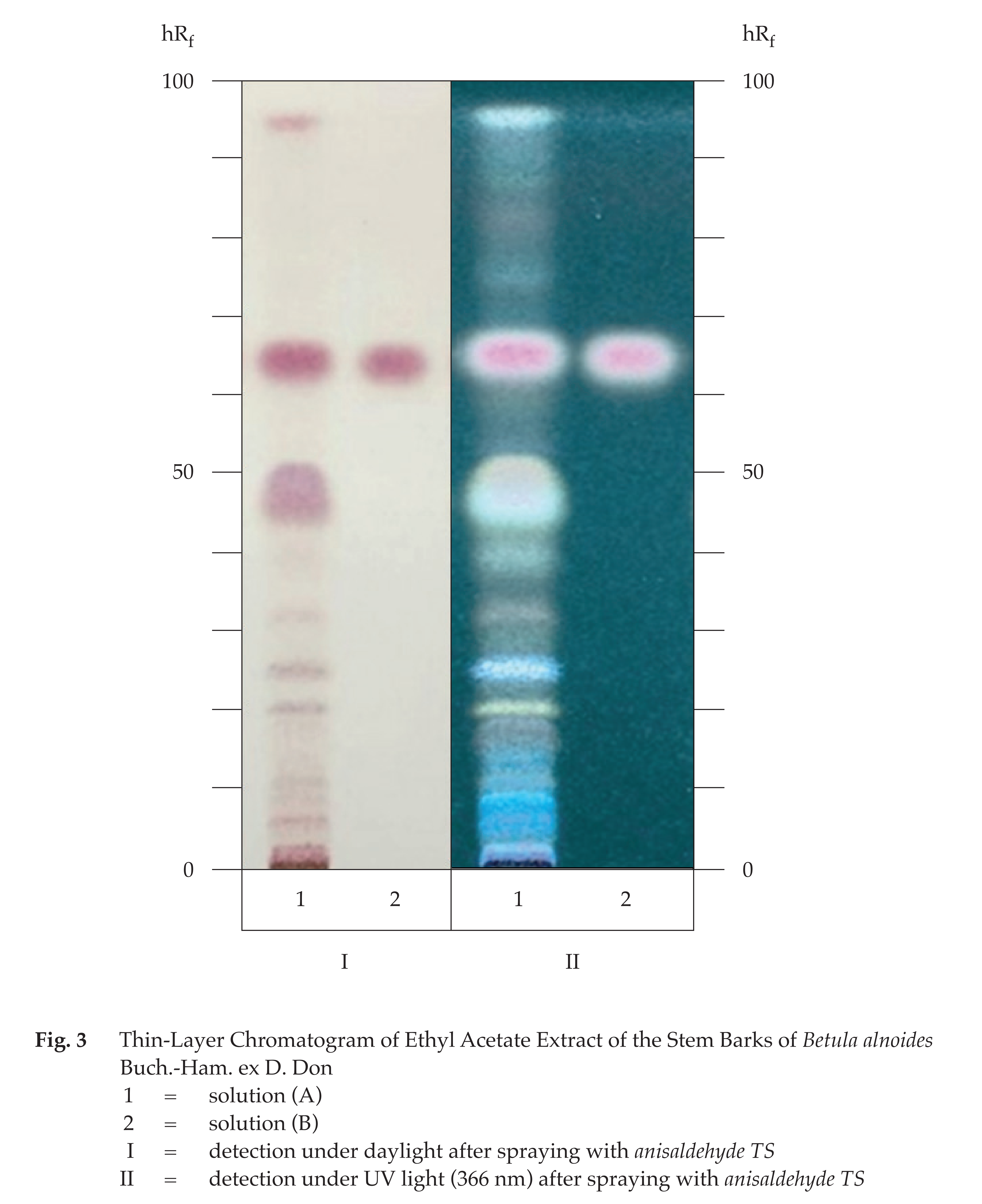
C. Carry out the test as described in the “Thin-Layer Chromatography” (Appendix 3.1), using silica gel GF254 as the coating substance and chloroform as the mobile phase and allowing the solvent front to ascend 8 cm above the line of application. Apply separately to the plate as bands of 5 mm, 4 µL each of solutions A and B. Prepare solution (A) by refluxing 2 g of the sample, in No. 250 powder, with 30 mL of ethyl acetate for 15 minutes and filtering. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness, dissolve the residue in 2 mL of methanol. For solution (B), dissolve 1 mg of lupeol in 1 mL of methanol. After removal of the plate, allow it to dry in air. Spray the plate with anisaldehyde TS and heat at 105° for 5 minutes and examine under daylight; the band corresponding to lupeol is purple (hRf value 62 to 67). Nine purple bands are also observed. Subsequently examine the same plate under ultraviolet light (366 nm); the band due to lupeol shows purple fluorescence; two yellow and seven blue fluorescent bands are also observed (Fig. 3).
Loss on drying Not more than 9.0 per cent w/w after drying at 105° to constant weight (Appendix 4.15).
Foreign matter Not more than 2.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.2).
Total ash Not more than 3.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.7).
Ethanol-soluble extractive Not less than 12.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.12).
Water-soluble extractive Not less than 8.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.12).