ตำรามาตรฐานยาสมุนไพรไทย
Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia
สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข
Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health(Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook.f. & Thomson)
(Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.)
(Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.)
(Centella Dry Extract)
(Centella Cream)
(Mesua ferrea L.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Pterocarpus santalinus L. f.)
(Santalum album L.)
(Senna tora (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna alata (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna Alata Tea)
(Piper retrofractum Vahl)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees)
(Andrographis Capsules)
(Allium ascalonicum L.)
(Ocimum tenuiflorum L.)
(Curcuma longa L.)
(Turmeric Capsules)
(Turmeric Dry Extract)
(Turmeric Dry Extract Capsules)
(Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.)
(Curcuma sp.)
Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.
(Aristolochia pierrei Lecomte)
(Zingiber officinale Roscoe)
(Ginger Capsules)
(Ginger Tea)
(Cassia fistula L.)
(Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC.)
(Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels)
Artemisia annua L.
(Ligusticum sinense Oliv. cv. Chuanxiong)
(Neopicrorhiza scrophulariiflora Pennell)
(Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC.)
(Aucklandia lappa Decne)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Angelica dahurica (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook. f. ex Franch. & Sav. var. dahurica)
(Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker)
(Hibiscus sabdariffa L.)
(Roselle Tea)
(Allium sativum L.)
(Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Sm.)
(Wurfbainia testacea (Ridl.) Škorničk.& A. D. Poulsen)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S. C. Chen)
(Ficus racemosa L.)
(Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit.)
Clerodendrum indicum (L.) Kuntze
(Phyllanthus emblica L.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Areca catechu L.)
(Momordica charantia L.)
Moringa oleifera Lam.
(Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa)
(Solanum trilobatum L.)
(Morus alba L.)
Gynostemma pentaphyllum(Thunb.)
Makino
(Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau)
(Cissus quadrangularis L.)
(Mimusops elengi L.)
(Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link. ex A. Dietr.)
(Piper betle L.)
(Capsicum annuum L.)
(Capsicum Oleoresin)
(Capsicum Gel)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Eurycoma longifolia Jack)
(Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl.)
(Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz.)
Senna garrettiana (Craib) H. S. Irwin & Barneby
(Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb.)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) H. Roxb.)
(Tarlmounia elliptica (DC.) H. Rob., S. C. Keeley, Skvaria & R. Chan)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract Capsiles)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract)
(Brachypterum scandens (Roxb.) Miq.)
(Lepidium sativum L.)
(Nigella sativa L.)
(Cuminum cyminum L.)
(Foeniculum vulgare Mill.)
(Plantago ovata Forssk.)
(Pimpinella anisum L.)
(Carum carvi L.)
(Anethum graveolens L.)
(Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague)
Albizia procera (Roxb.) Benth.
(Acorus calamus L.)
(Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels)
Cyanthillium cinereum (L.) H. Rob.
(Orthosiphon aristatus (Blume) Miq.)
Murdannia loriformis (Hassk.) R. S. Rao & Kammathy
(Capparis micracantha DC.)
(Chrysopogon zizanioides (L.) Roberty)
(Cyperus rotundus L.)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. & L. M. Perry)
(Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf.)
(Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl)
(Acanthus ilicifolius L.)
(Kaempferia galanga L.)
(Curcuma comosa Roxb.)
Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don
Cannabis sativa L.
Carthamus tinctorius L
Mitragyna speciosa (Korth.) Havil
Mallotus repandus (Rottler) Müll. Arg
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
Baliospermum solanifolium (Burm.) Suresh
Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb
Boesenbergia kingii Mood & L. M. Prince
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senna alexandriana Mill. var. alexandriana
Cassia acutifolia Delile, Cassia angustifolia Vahl
Butea superba Roxb. ex Willd.
[Plaso superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Kuntze, Rudolphia superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Poir.
Pueraria candollei Graham
ex Benth. var. mirifica (Airy Shaw & Suvat.) Niyomdham
Streblus asper Lour.
Suregada multiflora (A. Juss.) Baill. (Gelonium
multiflorum A. Juss.
Plumbago zeylanica L.
Plumbago indica L.
Biancaea sappan (L.) Tod.
Ziziphus attopensis Pierre
Streblus asper Lour.
Justicia gendarussa Burm. f.
Enhalus acoroides (L. f.) Royle
Bridelia ovata Decne.
Tamarindus indica L.
Citrus × aurantiifolia (Christm.) Swingle
Garcinia mangostana L.
Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC
Persicaria odorata (Lour.) Soják
Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link ex A. Dietr.
Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anderson
Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr.
Citrus × aurantium L. ‘Som Sa’
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
This test is provided to determine compliance with the limits on Disintegration stated in the individual monographs except where the label states that the tablets or capsules are intended for use as troches, or are to be chewed, or are designed as modified-release dosage forms (Dissolution Test, Appendix 4.24). Determine the type of units under test from the labelling and from observation, and apply the appropriate procedure to six or more dosage units.
For the purposes of this test, disintegration does not imply complete solution of the unit or even of its active constituent. Complete disintegration is defined as that state in which no residue, except fragments of undissolved tablet coating or of capsule shell, remains on the screen of the test apparatus or adheres to the lower surface of the disc if a disc has been used; if any other residue remains, it consists of a soft mass having no palpably firm core.
Apparatus
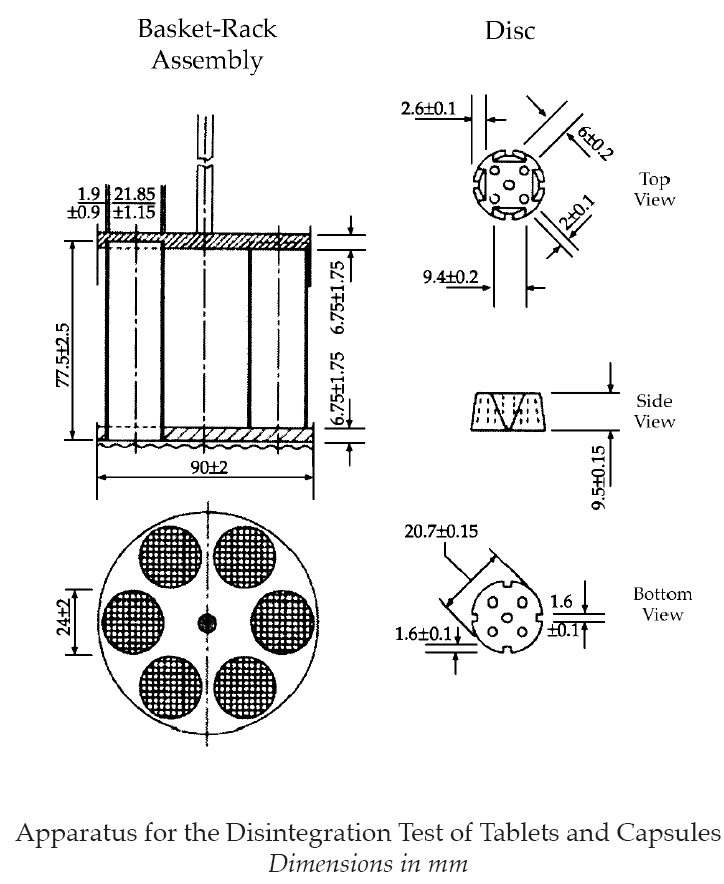
(a) A rigid basket-rack assembly supporting six open-ended cylindrical transparent tubes 77.5±2.5 mm long, approximately 21.85±1.15 mm in internal diameter and with a wall thickness of about 1.9±0.9 mm (see Figure).
(b) The tubes are held in a vertical position by two plates, each 90±2 mm in diameter and 6.75±1.75 mm in thickness, with six holes, each 24±2 mm in diameter, equidistant from the center of the plate and equally spaced from one another. Attached to the under surface of the lower plate is a woven stainless steel wire cloth, which has a plain square weave with 2.0±0.2 mm apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.615±0.045 mm.
(c) The parts of the apparatus are assembled and rigidly held by means of three bolts passing through the two plates. A suitable means is provided to suspend the basket-rack assembly from the raising and lowering device using a point on its axis. The device for raising and lowering the basket in the immersion fluid is set at a constant frequency rate between 29 and 32 cycles per minute through a distance of 55±2 mm.
(d) The apparatus consists of a basket-rack assembly, a 1000-mL, low-form beaker, 149±11 mm in height and having an inside diameter of 106±9 mm for theimmersion fluid, a thermostatic arrangement for heatingthe fluid between 37º±2º. The volume of the fluid in the vessel is such that at the highest point of the upward stroke the wire mesh remains at least 15 mm below the surface of the fluid and descends to not less than 25 mm from the bottom of the vessel on the downward stroke. At no time should the top of the basket-rack assembly become submerged. The time required for the upward stroke is equal to the time required for the downward stroke, and the change in stroke direction is a smooth transition, rather than an abrupt reversal of motion. The basket-rack assembly moves vertically along its axis. There is no appreciable horizontal motion or movement of the axis from the vertical. The design of the basket-rack assembly may be varied provided that the specifications for the tubes and wire mesh are maintained.
(e) A suitable device maintains the temperature of the liquid at 37º±2º, unless otherwise specified.
(f) The use of discs is permitted only where specified or allowed in the monograph. If specified in the individual monograph, each tube is provided with a cylindrical disc 9.5±0.15 mm thick and 20.7±0.15 mm in diameter. The disc is made of a suitable transparent plastic material having a specific gravity of between 1.18 and 1.20. Five parallel 2±0.1-mm holes extend between the ends of the cylinder. One of the holes is centered on the cylindrical axis. The other holes are centered 6±0.2 mm from the axis on imaginary lines perpendicular to the axis and parallel to each other. Four identical trapezoidal-shaped planes are cut into the wall of the cylinder, nearly perpendicular to the ends of the cylinder. The trapezoidal shape is symmetrical; its parallel sides coincide with the ends of the cylinder and are parallel to an imaginary line connecting the centers of two adjacent holes 6 mm from the cylindrical axis. The parallel side of the trapezoid on the bottom of the cylinder has a length of 1.6±0.1 mm, and its bottom edges lie at a depth of 1.6±0.1 mm from the cylinder’s circumference. The parallel side of the trapezoid on the top of the cylinder has a length of 9.4±0.2 mm, and its center lies at a depth of 2.6±0.1 mm from the cylinder’s circumference. All surfaces of the disc are smooth. If the use of discs is specified in the individual monograph, add a disc to each tube, and operate the apparatus as directed under Procedure. The discs conform to dimensions (see Figure).
Procedure
Select six units and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
UNCOATED TABLETS Introduce one tablet in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if prescribed, add a disc. Operate the apparatus, using water or the specified medium as the immersion fluid, maintained at 37º±2º. At the end of the 15-minute time limit unless otherwise specified in the monograph, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets have disintegrated completely. If one or two tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets. The requirement is met if not less than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested are disintegrated.
SOLUBLE TABLETS AND DISPERSIBLE TABLETS Introduce one tablet into each of the six tubes and operate the apparatus, using water at 20º±1º as the immersion fluid. The tablets disintegrate within 3 minutes unless otherwise stated in the individual monograph.
EFFERVESCENT TABLETS Place one tablet in a 50-mL beaker containing 200 mL of water at 20º±5º; numerous gas bubbles are evolved. When the evolution of gas around the tablet or its fragments has ceased the tablet shall have disintegrated, being either dissolved or dispersed in the water so that no agglomerates of particles remain. Repeat the operation on a further five tablets. The tablets comply with the test if each of the six tablets used in the test disintegrates in the manner prescribed within 5 minutes, unless otherwise stated in the individual monograph.
BUCCAL TABLETS Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. After 4 hours, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets have disintegrated. If one or two tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not less than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
SUBLINGUAL TABLETS Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. At the end of the time limit specified in the individual monograph: all of the tablets have disintegrated. If one or two tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not less
than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
COATED TABLETS Introduce one tablet into each of the six tubes, add disc to each tube, and operate the apparatus, using water as the immersion fluid. Unless otherwise stated in the individual monograph film-coated tablets disintegrate within 30 minutes and other coated tablets disintegrate within 60 minutes. For coated tablets other than film-coated tablets, if any of the tablets have not disintegrated, repeat the test on a further six tablets, replacing the water in beaker with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid. The tablets comply with the test
if all six tablets have disintegrated in the acid medium. For coated tablets including film-coated tablets, if the tablets fail to comply because of adherence of the tablets to the disc, repeat the test on a further six tablets omitting the discs. The tablets comply with the test if all six tablets have disintegrated.
DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS (ENTERIC-COATED TABLETS) Introduce one tablet in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if the tablet has a soluble external sugar coating, immerse the basket in water at room temperature for 5 minutes. Then operate the apparatus using simulated gastric fluid TS maintained at 37º±2º as the immersion fluid. After 2 hours of operation in simulated gastric fluid TS, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: the tablets show no evidence of disintegration, cracking, or softening. Operate the apparatus, using simulated intestinal fluid TS maintained at 37º±2º as the immersion fluid, for 60 minutes unless otherwise specified in the monograph. Lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets disintegrate completely. If one or two tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not less than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
HARD CAPSULES Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. Attach a removable wire cloth, which has a plain squareweave with 2±0.2-mm mesh apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.615±0.045 mm, as described under Apparatus, to the surface of the upper plate of the basket-rack assembly. Observe the capsules within 30 minutes unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph: all of the capsules have disintegrated except for fragments from the capsule shell.
If one or two capsules fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional capsules: not less than 16 of the total of 18 capsules tested disintegrate completely.
SOFT CAPSULES Proceed as directed under Hard Capsules.
DELAYED-RELEASE CAPSULES (ENTERIC CAPSULES) Introduce one capsule into each of the six tubes and unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph operate the apparatus for 2 hours1, using 0.1 M hydrochloric acid as the immersion fluid. No capsule shows signs of disintegration or of rupture permitting the escape of the contents. Change the immersion fluid to mixed phosphate buffer pH 6.8 and operate the apparatus for a further 60 minutes. The capsules pass the test if all six have disintegrated.
1The time of resistance to the acid medium varies according to the formulation of the preparation being examined. It is normally 3 hours but even with authorized deviations it is not less than 1 hour.