ตำรามาตรฐานยาสมุนไพรไทย
Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia
สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข
Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health(Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook.f. & Thomson)
(Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.)
(Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.)
(Centella Dry Extract)
(Centella Cream)
(Mesua ferrea L.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Piper sarmentosum Roxb.)
(Pterocarpus santalinus L. f.)
(Santalum album L.)
(Senna tora (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna alata (L.) Roxb.)
(Senna Alata Tea)
(Piper retrofractum Vahl)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees)
(Andrographis Capsules)
(Allium ascalonicum L.)
(Ocimum tenuiflorum L.)
(Curcuma longa L.)
(Turmeric Capsules)
(Turmeric Dry Extract)
(Turmeric Dry Extract Capsules)
(Arcangelisia flava (L.) Merr.)
(Curcuma sp.)
Harrisonia perforata (Blanco) Merr.
(Aristolochia pierrei Lecomte)
(Zingiber officinale Roscoe)
(Ginger Capsules)
(Ginger Tea)
(Cassia fistula L.)
(Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC.)
(Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels)
Artemisia annua L.
(Ligusticum sinense Oliv. cv. Chuanxiong)
(Neopicrorhiza scrophulariiflora Pennell)
(Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC.)
(Aucklandia lappa Decne)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Angelica dahurica (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook. f. ex Franch. & Sav. var. dahurica)
(Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker)
(Hibiscus sabdariffa L.)
(Roselle Tea)
(Allium sativum L.)
(Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Sm.)
(Wurfbainia testacea (Ridl.) Škorničk.& A. D. Poulsen)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Myristica fragrans Houtt)
(Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S. C. Chen)
(Ficus racemosa L.)
(Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit.)
Clerodendrum indicum (L.) Kuntze
(Phyllanthus emblica L.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Citrus hystrix DC.)
(Areca catechu L.)
(Momordica charantia L.)
Moringa oleifera Lam.
(Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa)
(Solanum trilobatum L.)
(Morus alba L.)
Gynostemma pentaphyllum(Thunb.)
Makino
(Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau)
(Cissus quadrangularis L.)
(Mimusops elengi L.)
(Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link. ex A. Dietr.)
(Piper betle L.)
(Capsicum annuum L.)
(Capsicum Oleoresin)
(Capsicum Gel)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Piper nigrum L.)
(Eurycoma longifolia Jack)
(Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl.)
(Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz.)
Senna garrettiana (Craib) H. S. Irwin & Barneby
(Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb.)
(Terminalia chebula Retz.)
(Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) H. Roxb.)
(Tarlmounia elliptica (DC.) H. Rob., S. C. Keeley, Skvaria & R. Chan)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract Capsiles)
(Hog Creeper Vine Dry Extract)
(Brachypterum scandens (Roxb.) Miq.)
(Lepidium sativum L.)
(Nigella sativa L.)
(Cuminum cyminum L.)
(Foeniculum vulgare Mill.)
(Plantago ovata Forssk.)
(Pimpinella anisum L.)
(Carum carvi L.)
(Anethum graveolens L.)
(Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague)
Albizia procera (Roxb.) Benth.
(Acorus calamus L.)
(Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels)
Cyanthillium cinereum (L.) H. Rob.
(Orthosiphon aristatus (Blume) Miq.)
Murdannia loriformis (Hassk.) R. S. Rao & Kammathy
(Capparis micracantha DC.)
(Chrysopogon zizanioides (L.) Roberty)
(Cyperus rotundus L.)
(Cannabis sativa L.)
(Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. & L. M. Perry)
(Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf.)
(Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl)
(Acanthus ilicifolius L.)
(Kaempferia galanga L.)
(Curcuma comosa Roxb.)
Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don
Cannabis sativa L.
Carthamus tinctorius L
Mitragyna speciosa (Korth.) Havil
Mallotus repandus (Rottler) Müll. Arg
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. var. siamensis Valeton
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
Baliospermum solanifolium (Burm.) Suresh
Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb
Boesenbergia kingii Mood & L. M. Prince
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senegalia rugata (Lam.) Britton & Rose
Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC.
Senna alexandriana Mill. var. alexandriana
Cassia acutifolia Delile, Cassia angustifolia Vahl
Butea superba Roxb. ex Willd.
[Plaso superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Kuntze, Rudolphia superba (Roxb. ex Willd.) Poir.
Pueraria candollei Graham
ex Benth. var. mirifica (Airy Shaw & Suvat.) Niyomdham
Streblus asper Lour.
Suregada multiflora (A. Juss.) Baill. (Gelonium
multiflorum A. Juss.
Plumbago zeylanica L.
Plumbago indica L.
Biancaea sappan (L.) Tod.
Ziziphus attopensis Pierre
Streblus asper Lour.
Justicia gendarussa Burm. f.
Enhalus acoroides (L. f.) Royle
Bridelia ovata Decne.
Tamarindus indica L.
Citrus × aurantiifolia (Christm.) Swingle
Garcinia mangostana L.
Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC
Persicaria odorata (Lour.) Soják
Zingiber montanum (J. König) Link ex A. Dietr.
Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anderson
Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr.
Citrus × aurantium L. ‘Som Sa’
Punica granatum L.
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz
the specifications given below are strictly for the use of the materials as reagents. The inclusion of a material in this Appendix does not imply that it is suitable for use in medicines. Exceptionally, a trademark or supplier may be indicated for certain reagents whose availability is limited. It is however acceptable to use reagents from another source provided that they comply with the standards of the Pharmacopoeia.
1.1 REAGENTS
The name of a substance or solution indicates a reagent included in the following list. The specifications given for reagents do not necessarily gurantee their quality for use in medicines.
Some of the reagents included may be injurious to health. Important cautions have been stated for these reagents. They should be handled in accordance with good laboratory
practice and any relevant regulations.
Reagents in aqueous solution are prepared using water. Where the name of the solvent is not stated, an aqueous solution is intended.
Unless otherwise specified, the reagents and reagent solutions are to be stored in well closed containers. The labelling should comply with the relevant national legislation.
Absorbent Cotton
Use a suitable grade.
Acetic Acid To glacial acetic acid,add sufficient water to produce a solution containing 33.0 per cent w/w of C2H4O2.
Acetic Acid, Glacial C2H4O2 = 60.05
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 99.5 per cent w/w and
not more than 100.5 per cent w/w of C2H4O2.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid; odour, pungent and characteristic. Boils at about 118°
Acetic Anhydride C4H6O3 = 102.09
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 97.0 per cent w/v of C4H6O3.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid.
BOILING RANGE 136° to 142° (Appendix 4.5).
Acetone C3H6O = 58.08
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless, mobile, volatile liquid; odour, characteristic. Flammable.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water, with chloroform, with ethanol, and with ether.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 55.5° and 57.0° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.790 to 0.792 g (Appendix 4.9).
ACIDITY Dilute 10.0 mL with 10.0 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. The solution requires for neutralization not more than 0.20 mL of 0.10 M sodium hydroxide, using phenolphthalein TS as indicator.
ALKALINITY Dilute 10 mL with 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. The solution is not alkaline to litmus paper.
WATER Shake 10.0 mL with 40.0 mL of carbon disulfide: a clear solution is produced.
OXIDIZABLE SUBSTANCES To 20.0 mL add 0.10 mL of 0.020 M potassium permanganate, and allow to stand for 15 minutes: the solution is not completely decolorized.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
Acetonitrile (Methyl Cyanide) C2H3N = 41.05
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water.
ACIDITY OR ALKALINITY A 10 per cent v/v solution is neutral to litmus.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 80° and 82° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.780 to 0.783 g (Appendix 4.9).
Aluminium Oxide, Neutral Al2O3 = 102.0
Use chromatographic grade of neutral activated alumina designed for column chromatography.
Ammonia Solution, Strong NH3 = 17.03
Contains not less than 25.0 per cent w/w and not more than 30.0 per cent w/w of NH3 and about 13.6 M in strength.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid, very caustic.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water and with methanol.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Relative density: 0.892 to 0.910.
B. It is strongly alkaline.
C. To 0.5 mL add 5 mL of water. Bubble air through the solution and lead the gaseous mixture obtained over the surface of a solution containing 1 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and 0.05 mL of methyl red TS. The colour changes from red to yellow. Add 1 mL of sodium cobaltinitrite TS: a yellow precipitate is formed.
TESTS Solution S for testing chloride, sulfate iron and heavy metals is prepared by evaporating 220 mL almost to dryness on a water-bath. Cool, add 1 mL of dilute acetic acid and dilute to 20 mL with distilled water.
APPEARANCE OF SOLUTION To 2 mL add 8 mL of water. The solution is clear and colourless.
OXIDIZABLE SUBSTANCES Cautiously add, whilst cooling, 8.8 mL to 100 mL of dilute sulfuric acid. Add 0.75 mL of 0.002 M potassium permanganate. Allow to stand for 5 minutes. The solution remains faintly pink.
PYRIDINE AND RELATED SUBSTANCES Not more than 2 ppm, calculated as pyridine. Measure the absorbance (Appendix 2.2) at 252 nm using water as the compensation liquid. The absorbance is not greater than 0.06.
CARBONATES Not more than 60 ppm. To 10 mL in a test-tube with a ground-glass neck add 10 mL of calcium hydroxide TS. Stopper immediately and mix. Any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a standard prepared at the same time and in the same manner using 10 mL of a 0.01 per cent w/v solution of anhydrous sodium carbonate.
CHLORIDE Not more than 1 ppm. Dilute 5 mL of Solution S to 15 mL with water. The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Chloride” (Appendix 5.2).
SULFATE Not more than 5 ppm. Dilute 3 mL of Solution S to 15 mL with distilled water. The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Sulfate” (Appendix 5.2).
IRON Not more than 0.25 ppm. Dilute 4 mL of Solution S to 10 mL with water. The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Iron” (Appendix 5.2).
HEAVY METALS Not more than 1 ppm. Dilute 4 mL of Solution S to 20 mL with water. The 12-mL solution complies with the “Limit Tes t for Heavy Metals” (Method I, Appendix 5.2). For the Standard Preparation, use lead standard solution (2 ppm Pb).
NON-VOLATILE MATTER Not more than 0.002 per cent w/v. A 50-mL sample, when evaporated and dried at 100° to 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 1.0 mg of residue.
ASSAY Weigh accurately a flask with a ground-glass neck containing 50.0 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid VS. Add 2 mL of the substance to be examined and reweighed. Add 0.1 mL of methyl red TS as indicator. Titrate with 1 M sodium hydroxide VS until the colour changes from red to yellow. Each mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 17.03 mg of NH3.
Store protected from air, at a temperature not exceeding 20°.
Ammonium Dihydrogenphosphate (Ammonium Phosphate, Monobasic)(NH4)H2PO4 = 115.03
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce.
pH About 4.2, in a 2.3 per cent w/v solution (Appendix 4.11).
Andrographolide C20H30O5 = 350.46
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of C20H30O5.
DESCRIPTION Colourless or white rhombic prisms or plates.
SOLUBILITY Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in chloroform, in ether and in methanol.
Anethole C10H12O = 148.20
DESCRIPTION Colourless or fainly yellow liquid at or above 23°; adour aromatic. Affected by light.
SOLUBILITY Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in ethanol; readily miscible with chloroform and with ether.
FREEZING TEMPERATURE Not lower than 20° (Appendix 4.4).
BOILING RANGE 231° to 237° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.557 to 1.561 (Appendix 4.7).
OPTICAL ROTATION –0.15° to +0.15° (Appendix 4.8).
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 0.983 to 0.988 (Appendix 4.9).
HEAVY METALS Not more than 40 ppm (Method II, Appendix 5.2). Use 1.0 g; for the Standard Preparation; use lead acetate solution (2 ppm Pb).
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Shake 10 mL with 50 mL of saturated solution of sodium hydrogensulfite in a graduated cylinder, and allow the mixture to stand for 6 hours: no appreciable diminution in the volume of anethole occurs, and no crystalline deposit separates.
PHENOLS Shake 1 mL with 20 mL of water, and allow the liquids to separate. Filter the water layer through a filter paper previously moistened with water and to 10 mL of the filtrate add 3 drops of iron(III) chloride TS: no purple or purplish colour is produced.
Anisaldehyde (4-Methoxybenzaldehyde) C8H8O2 = 136.15
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless or pale yellow, oily liquid; odour, aromatic.
SOLUBILITY Slightly soluble in water; miscible with ethanol and with ether.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 248° (Appendix 4.6).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.125 g (Appendix 4.9).
Antimony Trichloride SbCl3 = 228.11
Contains not less than 97.0 per cent of SbCl3.
DESCRIPTION Colourless crystals, fuming in moist air.
SOLUBILITY Very soluble in absolute ethanol and in chloroform, forming solutions which are not more than slightly turbid.
ASSAY Dissolve about 500 mg, accurately weighed, in 30 mL of water containing 4 g of potassium sodium tartrate, add 2 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate and titrate with 0.05 M iodine VS, using starch TS as indicator near the end of the titration. Each mL of 0.05 M iodine VS is equivalent to 11.41 mg of SbCl3.
L-Arabinose C5H10O5 = 150.13
DESCRIPTION White, crystalline powder.
SPECIFIC ROTATION About +104° at 20°, determined in a 5 per cent w/v solution (Appendix 4.8).
Artemisinin C15H22O5 = 282.33
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent of C15H22O5.
Store in a cool place.
β-Asarone (1,2,4-Trimethoxy-5-(1-propenyl) benzene; 2,4,5-Trimethoxy-1-propenylbenzene) C12H16O3 = 208.26
Use a suitable grade.
Astragalin (Kaempferol 3-β-D-glucopyranoside) C21H20O11 = 448.38
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less the 97.0 per cent.
DESCRIPTION White to light yellow powder or crystals.
SOLUBILITY Sparingly soluble in ethanol and methanol.
MELTING RANGE 218° to 220° (Appendix 4.3)
Store in tightly closed containers at a temperature between 2° and 8°.
Asiatic Acid C30H48O5 = 488.70
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C30H48O5.
Asiaticoside C48H78O19 = 959.12
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 97.0 per cent of C48H78O19.
Benzene C6H6 = 78.11
DESCRIPTION Colourless, transparent liquid. Flammable.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent dis tils between 79.5° and 81° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.876 to 0.881 g (Appendix 4.9).
SULFUR COMPOUNDS Boil 10 mL with 1 mL of absolute ethanol and 3 mL of potassium plumbite TS for 15 minutes under reflux conderser, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. The aqueous layer remains colourless.
THIOPHENE Shake 2 mL with 15 mL of sulfuric acid containing 3 mg of isatin in a stoppered tube for 5 minutes and allow to separate. No blue or green colour is produced.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
Berberine Chloride C20H18ClNO4·2H2O = 407.85
DESCRIPTION Yellow crystals.
MELTING RANGE 204° to 206° (Appendix 4.3).
Bismuth Oxynitrate (Bismuth Subnitrate) Bi5O(OH)9(NO3)4 = 1461.99
DESCRIPTION White, microcrystalline powder.
SOLUBILITY Insoluble in water and in ethanol; readily soluble in dilute nitric acid and in dilute hydrochloric acid.
1-Butanol (n-Butyl Alcohol) C4H10O = 74.12
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Soluble at 15.5° in 11 parts of water.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 116° and 119° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.807 to 0.810 g (Appendix 4.9).
FLUORESCENCE When examined under screened ultraviolet light, shows not more than the faintest trace of fluorescence.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
Caffeic Acid C9H8O4 = 180.16
DESCRIPTION White or almost white, crystals or plates.
SOLUBILITY Freely soluble in hot water and in ethanol; sparingly soluble in cold water.
MELTING TEMPERATURE About 210°, with decomposition (Appendix 4.3).
Capsaicin C18H27NO3 = 342.85
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C18H27NO3.
Carbophenothion C11H16ClO2PS3 = 305.41
Use a suitable grade for pesticide resdue analysis. A certified reference material (10 ng/mL in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane) may be used.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.27 g (Appendix 4.9).
Carvone C10H14O = 150.22
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Liquid.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water; miscible with ethanol.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 230° (Appendix 4.6).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.500 (Appedix 4.7).
SPECIFIC ROTATION +61° (Appendix 4.8).
RELATIVE DENSITY 0.965 (Appendix 4.9).
(+)-Catechin C15H14O6 = 290.27
MELTING TEMPERATURE 210° (Appendix 4.3).
(+)-Catechin Hydrate C15H14O6.xH2O= 290.27
MELTING TEMPERATURE 175° to 177° (Appendix 4.3).
Charantin
Use a suitable grade.
Charcoal, Decolorizing
DESCRIPTION Black, light powder free from grittiness.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in all usual solvents.
DECOLORIZING POWER Dissolve 100 mg of strychnine sulfate in 50 mL of water, add 1 g of the test substance, shake during 5 minutes, and pass through a dry filter the first 10 mL of the filtrate. To a 10-mL portion of the subsequent filtrate add 1 drop of hydrochloric acid and 5 drops of mercuric-potassium iodide TS: no turbidity is produced.
ACID-SOLUBLE MATTER Not more than 3 per cent w/w. To 1.0 g add 25 mL of dilute nitric acid and boil for 5 minutes. Filter whilst hot through a sintered-glass filter of porosity of 4 to 10 μm and wash with 10 mL of hot water. Evaporate the combined filtrate and washings to dryness on a water-bath, add to the residue 1 mL of hydrochloric acid, evaporate to dryness again and dry the residue to cons tant weight at 100° to 105°. The residue weighs not more than 30 mg.
SULFATED ASH Not more than 5.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 5.3).
Chloroform CHCl3 = 119.38
| Caution Care should be taken not to vaporize chloroform in the presence of a flame, because of the production of harmful gases. |
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing 0.4 to 1.0 per cent w/v of ethanol.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, volatile liquid; odour, characteristic.
SOLUBILITY Slightly soluble in water; miscible with absolute ethanol, with ether, with fixed and volatile oils, and with most organic solvents.
RELATIVE DENSITY 1.475 to 1.481 (Appendix 4.9).
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 60° (Appendix 4.6).
Store protected from light.
Chloroform Water Shake 2.5 mL of chloroform with 900 mL of water until dissolved and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Citral C10H16O = 152.24
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C10H16O.
Citronellal C10H18O = 154.25
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of C10H18O.
SOLUBILITY Very slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol.
REFRACTIVE INDEX About 1.446, at 20° (Appendix 4.7).
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 0.848 to 0.856 (Appendix 4.9).
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool and dry place, protected from light.
Citronellol C10H20O = 156.27
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of C10H20O.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol.
BOILING RANGE 220° to 222° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.456, at 20° (Appendix 4.7).
SPECIFIC GRAVITY About 0.857 (Appendix 4.9).
Store in tightly closed containers, protected from light.
Citronellyl Acetate C12H22O2 = 198.30
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of C12H22O2.
BOILING POINT 229° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.443, at 20° (Appendix 4.7).
SPECIFIC GRAVITY About 0.89 (Appendix 4.9).
Store in tightly closed containers, protected from light.
Cuminaldehyde [4-(1-Methylethyl)benzaldehyde; p-Isopropylbenzaldehyde]
C10H12O = 148.20
DESCRIPTION Colourless to yellowish, oily liquid; odour, s trong persis tent; tas te, acrid burning taste.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol and in ether.
BOILING RANGE 235° to 236° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.5301 (Appendix 4.7).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 0.978 g (Appendix 4.9).
Curcumin C21H20O6 = 368.39
Use a general reagent grade of commerce containing a mixture of curcumin, desmethoxycurcumin and bisdesmethoxycurcumin.
DESCRIPTION Orange-brown, crystalline powder.
SOLUBILITY Insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol.
THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAM
System A ___ benzene:chloroform:ethanol 49:49:2
hRf value ___ curcumin 28-34
desmethoxycurcumin 17-20
bisdesmethoxycurcumin 11-15
System B ___ toluene:chloroform:absolute ethanol 49:49:2
hRf value ___ curcumin 24-26
desmethoxycurcumin 12-15
bisdesmethoxycurcumin 6-8
Cyclohexane C6H12 = 84.16
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 80° and 82° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.4262 to 1.4265, at 20° (Appendix 4.7).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.776 to 0.780 g (Appendix 4.9).
1,2-Dichloroethane (Ethylene Chloride) C2H4Cl2 = 98.96
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid; odour, chloroform-like.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 2 parts of ethanol yielding a clear, colourless solution.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 82° and 84° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.25 g (Appendix 4.9).
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
Dichloromethane (Methylene Chloride) CH2Cl2 = 84.93
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless, mobile liquid.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 50 parts of water; miscible with ethanol and with ether.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 39° and 41° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 1.323 to 1.325 g (Appendix 4.9).
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.05 per cent w/v of residue.
Diethanolamine C4H11NO2 = 105.14
DESCRIPTION Colourless or slightly tinted liquid.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water, with acetone, with chloroform, with ethanol, and with glycerol; slightly soluble to insoluble in ether and in petroleum ether.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 217° (Appendix 4.6).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.1 g (Appendix 4.9).
pH 10.0 to 11.5, determined in a 5.0 per cent w/v solution (Appendix 4.11).
OTHER REQUIREMENTS Diethanolamine intended for alkaline phosphatase tes t complies with the following additional requirement.
MONOETHANOLAMINE Not more than 1.0 per cent w/w when determined in the following manner. Dissolve 1.00 g of 3-aminopropanol (internal standard) in sufficient acetone to produce 10.0 mL (solution A). Dissolve 500 mg of monoethanolamine in sufficient acetone to produce 10.0 mL (solution B). Carry out the determination as described in the “Gas Chromatography” (Appendix 3.4), using the following solutions. For solution (1) add 1.0 mL of solution A to 5.00 g of the test substance and dilute to 10 mL with acetone. For solution (2) dissolve 5.00 g of the test substance in sufficient acetone to produce 10 mL. For solution (3) add 1.0 mL of solution A to 0.5 mL of solution B and dilute to 10 mL with acetone. Prepare solution (4) in the same manner as solution (3) but adding 1.0 mL of solution B in place of 0.5 mL of solution B. Prepare solution (5) in the same manner as solution (3) but adding 2.0 ml of solution B in place of 0.5 mL of solution B. The chromatographic procedure may be carried out using a column (1 m × 4 mm) packed with diphenylphenylene oxide porous polymer beads (180- to 250-μm) and the carrier gas with the flow rate of mL per minute. Maintain the temperature of the column at 125° for 3 minutes and then raise to 300° at a rate of 12° per minute. Maintain the temperature of the injection port at 250° and that of the detector at 280°.
Diethylamine C14H11N = 73.14
| Caution May be irritating to skin and mucous membranes. |
Contains not less than 99.5 per cent of C14H11N.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid. Flammable.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.702 to 0.704 g (Appendix 4.9).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.384 to 1.386 (Appendix 4.7).
ASSAY Add about 3 g, accurately weighed, to 50.0 mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid VS and titrate the excess of acid with 1 M sodium hydroxide VS, using methyl red TS as indicator. Each mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid VS is equivalent to 73.14 mg of C14H11N.
Diethyl ether C4H10O = 74.12
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid; odour, characteristic.
BOILING POINT 34.6° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.71 g (Appendix 4.9).
3,5-Dinitrobenzoic Acid C7H4N2O6 = 212.12
DESCRIPTION Practically colourless crystals.
SOLUBILITY Slightly soluble in water; very soluble in ethanol.
MELTING RANGE 205° to 207° (Appendix 4.3).
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine C6H6N4O4 = 198.14
DESCRIPTION Orange-red crystals, or crystalline powder, which under the microscope appear individually to be lemon-yellow, lath-like needles.
SOLUBILITY Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol; moderately soluble in dilute inorganic acids.
MELTING RANGE 197° to 200°, with decomposition (Appendix 4.3).
SOLUBILITY TEST Dissolve 500 mg in a mixture of 25 mL of sulfuric acid and 25 mL of water: the solution is clear or not more than slightly turbid.
SULFATED ASH Negligible (Appendix 5.3); use 500 mg.
Diphenylboric Acid Aminoethyl Ester (Diphenylboric Acid β-Aminoethyl Ester;
Diphenylboric Acid-Ethanolamine Reagent) C14H16BNO = 225.10
Use a suitable grade.
Emodin C15H10O5 = 270.21
DESCRIPTION Orange crystals.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides; slightly soluble in ether.
MELTING TEMPERATURE About 253°, with decomposition (Appendix 4.3).
Estragole C10H12O = 148.20
Use a suitable grade.
Ethanol C2H6O = 46.07
Use Ethanol (95 Per Cent) (see under “Reagents”).
Ethanol (95 Per Cent)
A mixture of ethanol and water. Contains not less than 92.3 per cent w/w and not more than 93.8 per cent w/w, corresponding to not less than 94.9 per cent v/v and not more than 96.0 per cent v/v, at 15.56°, of C2H6O.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, clear, mobile and volatile liquid; odour, characteris tic and spirituous. Flammable, burning with a blue smokeless flame.Boils at about 78°.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water, with chloroform and with ether.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Mix 5 drops in a small beaker with 1 mL of potassium permanganate TS and 5 drops of dilute sulfuric acid and cover the beaker immediately with a filter paper moistened with a solution recently prepared by dissolving 100 mg of sodium nitroferricyanide and 500 mg of piperazine hydrate in 5 mL of water: an intense blue colour is produced on the filter paper, the colour becoming paler after a few minutes.
B. To 5 mL of a 0.5 per cent v/v solution, add 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide; then slowly add 2 mL of iodine TS: the odour of iodoform develops and a yellow precipitate is produced.
ACIDITY OR ALKALINITY To 20 mL add 5 drops of phenolphthalein TS: the solution remains colourless and requires not more than 0.20 mL of 0.10 M sodium hydroxide to produce a pink colour.
CLARITY OF SOLUTION Dilute 5 mL to 100 mL with water in a glass cylinder: the solution remains clear when examined against a black background.
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Heat 100 mL of hydroxylamine TS in a loosely stoppered flask on a water-bath for 30 minutes,cool,and,if necessary, add sufficient 0.050 M sodium hydroxide to restore the green colour. To 50 mL of this solution add 25 mL of the sample and heat on a water-bath for 10 minutes in a loosely stoppered flask. Cool, transfer to a Nessler cylinder, and titrate with 0.050 M sodium hydroxide until the colour matches that of the remainder of the hydroxylamine solution contained in a similar cylinder, both solutions being viewed down the axis of the cylinder. Not more than 0.90 mL or 0.050 M sodium hydroxide is required.
OXIDIZABLE SUBSTANCES To 20 mL add 1 mL of 0.002 M potassium permanganate. Allow the
solution to s tand at 20° for 10 minutes protected from light: the colour is not completely
discharged.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER A 100-mL sample, when evaporated and dried at 100° to 105° to
cons tant weight, leaves not more than 2.5 mg of residue.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 0.805 to 0.821, at 25° (Appendix 4.9), using this result to ascertain the percentage of C2H6O contained in the liquid examined by reference to the Alcoholometric Table.
VOLATILE IMPURITIES Carry out the test as described in the “Gas Chromatography” (Appendix 3.4).
Reference solution (a) Dilute 100 mL of anhydrous methanol to 50.0 mL with the test substance. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the test substance.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 50 mL of anhydrous methanol and 50 mL of acetaldehyde to 50.0 mL with the test substance. Dilute 100 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the test substance.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 150 mL of acetal to 50.0 mL with the test substance. Dilute 100 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the test substance.
Reference solution (d) Dilute 100 mL of benzene to 100.0 mL with the test substance. Dilute 100 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the test substance.
Test solution (a) The test substance.
Test solution (b) Add 150 mL of 4-methyl-2-pentanol to 500.0 mL of the test substance.
Chromatographic system A gas chromatograph equipped with (a) a glass (fused silica) column (30 m × 0.32 mm) packed with porous poly[(cyanopropyl)(phenyl)][dimethyl]-siloxane (1.8mm), maintained as the following table, (b) a flame ionization detector main - tained at 280°, and (c) helium as the carries gas.
System suitability Chromatograph Reference solution (b) and record the peak response as directed for Procedure: the resolution between the first peak (acetaldehyde) and the second peak (methanol) is not less than 1.5.
Procedure Inject separately suitable volumes of each of Reference solution (a), Reference solution (b), Reference solution (c), Reference solution (d), Test solution (a), and Test solution (b).
Limits:
- methanol in the chromatogram obtained from test solution (a): not more than half the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained from reference solution (a) (200 ppm v/v),
- acetaldehyde + acetal: maximum 10 ppm v/v, expressed as acetaldehyde.
Calculation Calculate the sum of the contents of acetaldehyde and acetal in parts per million (v/v) using the following expression:
where AE = area of the acetaldehyde peak in the chromatogram obtained from test
solution (a),
AT = area of the acetaldehyde peak in the chromatogram obtained
from reference solution (b),
CE = area of the acetal peak in the chromatogram obtained from test solution (a),
and
CT = area of the acetal peak in the chromatogram obtained from reference
solution (c).
- benzene: maximum 2 ppm v/v.
Calculation Calculate the content of benzene in parts per million (v/v) using the following expression:
where BE = area of the benzene peak in the chromatogram obtained from the test
solution (a), and
BT = area of the benzene peak in the chromatogram obtained from reference
solution (d).
If necessary,the identity of benzene can be confirmed using another suitable chromatographic system (stationary phase with a different polarity).
- total of other impurities in the chromatogram obtained from test solution (b): not more than the area of the peak due to 4-methyl-2-pentanol in the chromatogram obtained from test solution (b) (300 ppm v/v),
- disregard limit: 0.03 times the area of the peak corresponding to 4-methyl-2-pentanol in the chromatogram obtained from test solution (b) (9 ppm v/v).
Ethanol, Absolute C2H6O = 46.07
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, clear, mobile and volatile liquid; odour, characteris tic and spirituous. Flammable, burning with a blue, smokeless flame. Hygroscopic.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water, with chloroform and with ether.
BOILING RANGE 78° to 79° (Appendix 4.5).
RELATIVE DENSITY 0.791 to 0.794 (Appendix 4.9).
Store protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 30°.
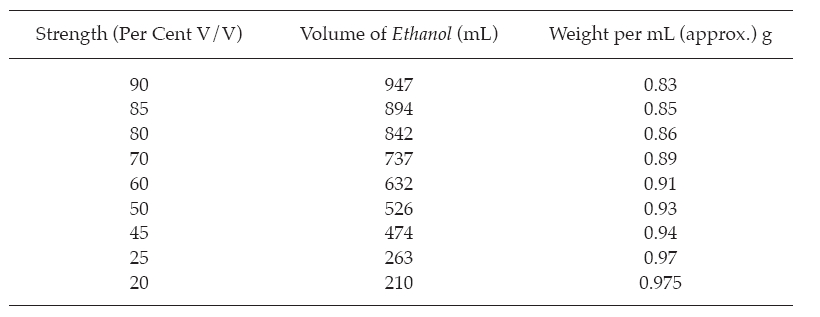
Ethanols, Diluted Prepare by diluting the volumes of ethanol indicated in the following table with water to 1000 mL.
Ether C4H10O = 74.12
| Caution Ether tends to form explosive peroxides, especially when anhydrous |
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless, volatile, very mobile liquid; odour, characteris tic. Highly flammable;mixtures of its vapour with oxygen, air, or nitrous oxide in certain concentrations are explosive.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 10 parts of water, miscible with benzene, with chloroform, with dichloromethane, with ethanol, with fixed oils, with petroleum ether, and with volatile oils.
PEROXIDES Transfer 8 mL of potassium iodide and starch TS to a stoppered tube of about 12-mL capacity and about 1.5 cm in diameter. Fill completely with the test substance, shake vigorously, and allow to stand in the dark for 30 minutes. No colour is produced.
Store protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 15°. The name and concentration of any added stabilizer are stated on the table.
Ethyl Acetate C4H8O2 = 88.11
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid; odour, fruity-like.
BOILING RANGE 76° to 78°(Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.901 to 0.904 g (Appendix 4.9).
Ethyl Formate C3H6O2 = 74.08
DESCRIPTION Mobile liquid.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 10 parts of water with gradual decomposition into free acid and ethanol; miscible with ethanol and with ether.
Store in tightly closed containers and preferably in contact with calcium chloride.
Eugenol C10H12O2 = 164.20
DESCRIPTION Colourless or pale yellow, oily liquid, darkening on exposure to air and light and becoming more viscous; odour, clove-like.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water; miscible with chloroform, with ethanol, with ether,and with fixed and volatile oils.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 250° (Appendix 4.6).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.068 g (Appendix 4.9).
Eurycomanone C20H24O9 = 408.40
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of C20H24O9.
DESCRIPTION White powder.
Store in tightly closed containers, protected from light and air, at a temperature not exceeding 20°.
Fenchone C10H16O = 152.23
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C10H16O.
Ferulic acid C10H10O4 = 194.18
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C10H10O4.
Formaldehyde Solution (Formalin) CH2O = 30.03
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 34.0 per cent w/v and not more than 37.0 per cent w/v of CH2O.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, aqueous solution with a lachrymatory vapour.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.08 g (Appendix 4.9).
Store at a temperature between 15° and 25°.
Formic Acid CH2O2 = 46.03
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing about 90 per cent w/w of CH2O2 and about 23.6 M in strength.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, corrosive liquid; odour, pungent.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.20 g (Appendix 4.9).
Formic Acid, Anhydrous CH2O2 = 46.03
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of CH2O2.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, corrosive liquid; odour, pungent.
RELATIVE DENSITY About 1.22 (Appendix 4.9).
D-Galactose C6H12O6 = 180.16
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION White crystalline or finely granulated powder.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in water; very slightly soluble in ethanol.
MELTING TEMPERATURE About 164°, with decomposition (Appendix 4.3).
SPECIFIC ROTATION About +80° at 20°, determined in a 10 per cent w/v solution containing about 0.05 per cent v/v of ammonia (Appendix 4.8).
Gallic Acid (3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid Monohydrate) C7H6O5·H2O = 188.14
DESCRIPTION White or almost white crystals or powder.
SOLUBILITY Sparingly soluble in cold water; very soluble in boiling water and in ethanol.
DISTINCTION FROM TANNIC ACID Its cold, saturated solution neither colours nor precipitates solutions of pure iron(II) salts and yields no precipitate with gelatin TS.
Gelatin
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless or slightly yellow, transparent, brittle, testeless sheets, flaske, or powder; odourless.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in hot water, acetic acid and glycerol; insoluble in organic solvents.
Geraniol C10H18O = 154.25
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 97.0 per cent w/w of C10H18O.
DESCRIPTION Oily liquid, slight odour of rose.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol.
Store in tightly closed containers, protected from light.
Geranyl Acetate C12H20O2 = 196.27
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 97.0 per cent w/w of C12H20O2.
DESCRIPTION Colourless or slightly yellow liquid, slight odour of rose and lavender.
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool and dry place.
6-Gingerol C17H26O4 = 294.39
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of C17H26O4.
DESCRIPTION Yellowish white or yellow liquid or solid.
Gypenoside III (Ginsenoside Rb1) C54H92O23·3H2O = 1163.34
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of C54H92O23·3H2O.
DESCRIPTION A colourless solid.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in water, in anhydrous ethanol and in methanol.
MELTING POINT About 199° (Appendix 4.3).
SPECIFIC ROTATION About + 11.3 determined in a 1 per cent w/v solution in methanol (Appendix 4.8).
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool and dry place.
Helium He = 4.00
Use a suitable laboratory cylinder grade of commerce containing not less than 99.995 percent v/v of He.
Helium for Chromatography
Use Helium.
Hexane C6H14 = 86.18
The hexane fraction from petroleum.
DESCRIPTION Colourless,mobile,highly flammable liquid.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 67° and 70° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.670 to 0.677 g (Appendix 4.9).
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
n-Hexane C6H14 = 86.18
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce usually containing not less than 99 per cent of the pure isomer, n-C6H14.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, flammable liquid.
BOILING RANGE Distils completely over a range of 1° between 67.5° and 69.5° (Appendix 4.5).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.374 to 1.375 (Appendix 4.7).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.658 to 0.659 g (Appendix 4.9).
Hide Powder
Use a suitable grade.
Hydrochloric Acid HCl = 36.46
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
When no molarity is indicated, use analytical reagent grade of commerce with a relative density of about 1.18, containing not less than 35 per cent w/w and not more than 38 percent w/w of HCl and about 11.5 M in strength.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless, fuming liquid; odour, pungent.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water.
Solutions of molarity xM should be prepared by diluting 85x mL of hydrochloric acid to 1000 mL with water.
Store in a container of polyethylene or other non-reacting material at a temperature not exceeding 30°.
Hydrochloric Acid, Dilute A 10 per cent w/v solution. Prepare by mixing 226 mL of hydrochloric acid with sufficient water to produce 1000 mL.
Hydrochloric Acid, Heavy Metal-Free
Use a suitable reagent grade of commerce. Complies with the requirements prescribed for hydrochloric acid with the following maximum contents of heavy metals in ppm: Arsenic 0.005, Cadmium 0.003, Copper 0.003, Iron 0.05, Mercury 0.005, Nickel 0.004, Lead 0.001, and Zinc 0.005.
Hydrochloric Acid, Dilute, Heavy Metal-Free
Use a suitable reagent grade of commerce. Complies with the requirements prescribed for hydrochloric acid with the following maximum contents of heavy metals in ppm: Arsenic 0.005, Cadmium 0.003, Copper 0.003, Iron 0.05, Mercury 0.005, Nickel 0.004, Lead 0.001, and Zinc 0.005.
Hydrogen Peroxide Solution, Strong H2O2 = 34.01
| Caution Strong Hydrogen Peroxide Solution decomposes vigorously in contact with oxidizable organic matter and with certain metals and if allowed to become alkaline. |
Contains not less than 29.0 per cent w/w and not more than 31.0 per cent w/w H2O2, corresponding to about 100 times its volume of available oxygen. It may be stabilized by adding a suitable preservative.
DESCRIPTION Colourless and almost odourless liquid.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Cautiously make the solution alkaline. It decomposes with vigorous effervescence.
B. Mix 1 drop with 2 mL of dilute sulfuric acid, 2 mL of ether and 1 drop of potassium chromate TS and shake. The ethereal layer is coloured deep blue.
ACIDITY Dilute 10.0 mL with 100 mL of water and add 5 drops of methyl red TS. Not less than 0.05 mL and not more than 0.50 mL of 0.10 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the solution.
ORGANIC PRESERVATIVE Shake 20.0 mL with 10 mL of chloroform and then with two successive 5-mL portions of chloroform. Evaporate the combined chloroform solutions under reduced pressure at a temperature not exceeding 25°, and dry in a desiccator. Any residue weighs not more than 10 mg.
BARIUM Dilute 1 mL to 10 mL with water and add 1 mL of dilute sulfuric acid. The solution remains clear for not less than 15 minutes.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.2 per cent w/v of residue.
ASSAY Dilute about 1 g, accurately weighed, to 100.0 mL with water. Add to 10.0 mL of this solution a cold mixture of 2.5 mL of sulfuric acid and 20 mL of water. Titrate with 0.02 M potassium permanganate VS. Each mL of 0.02 M potassium permanganate VS is equivalent to 1.701 mg of H2O2.
Store in a cool place, protected from light.
Imperatorin C16H14O4 = 270.28
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of C16H14O4.
DESCRIPTION off-white or light brown poder.
Iron(III) Chloride (Ferric Chloride) FeCl3·6H2O = 270.30
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Yellowish orange or brownish, crystalline masses; deliquescent.
Store in well-closed containers.
Iron(II) Sulfate (Ferrous Sulfate) FeCl4·7H2O = 278.01
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Bluish green crystals or pale, crystalline powder; odourless. Efflorescent in air. Oxidizes in moist air, becoming brown.
Store in well-closed containers
Iron(III) Sulfate Fe2(SO4)3·xH2O
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION White to yellow, hygroscopic powder which decomposes in air.
Store protected from light.
Lead(II) Acetate C4H6O4Pb·3H2O = 379.34
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Small, white, transparent, monoclinic prisms or heavy, crystalline masses; odour, acetous. Efflorescent in warm air. Becomes basic when heated.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 2 parts of water and in 63 parts of ethanol; freely soluble in glycerol.
Lead(II) Oxide (Lead Monoxide) PbO = 223.20
Use a suitable grade.
Lupeol C30H50O = 426.72
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
Madecassoside C48H78O20 = 975.12
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C48H78O20.
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool place.
Magnesium Mg = 24.305
DESCRIPTION Silvery white ribbon. It slowly oxidizes in moist air.
Magnesium Acetate C4H6MgO4·4H2O = 214.46
Contains not less than 99.0 per cent of C4H6MgO4·4H2O.
DESCRIPTION Colourless crystals.
pH 8.2 to 8.8, in a 5.0 per cent w/v solution (Appendix 4.11).
ASSAY Dissolve about 800 mg, accurately weighed, in 100 mL of water, add 10 mL of strong ammonia-ammonium chloride TS and 0.5 mL of mordant black 11 TS, and titrate at 40° with 0.1 M disodium edetate VS until the las t trace of red colour disappears and the solution becomes pure blue. Each mL of 0.1 M disodium edetate VS is equivalent to 21.45 mg of C4H6MgO4·4H2O.
Magnesium Nitrate (Magnesium Nitrate Hexahydrate) Mg(NO3)2·6H2O = 256.41
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, clear crystals, deliquescent.
SOLUBILITY Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol.
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool and dry place.
Magnesium Ribbon
Use a suitable grade.
Methanol (Methyl Alcohol) CH4O = 32.04
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water, forming a clear colourless liquid.
BOILING RANGE 64° and 65° (Appendix 4.5).
RELATIVE DENSITY 0.791 to 0.793° (Appendix 4.9).
L-Methionine C5H11NO2S = 149.21
DESCRIPTION White, crystalline solid.
SPECIFIC ROTATION About +23° at 20°, determined in a 5 per cent w/v solution in 1 M hydrochloric acid (Appendix 4.5).
Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether (2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane) C5H12O = 88.15
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool place, protected from light.
Nitric Acid HNO3 = 63.01
When no molarity is indicated, use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing about 70.0 per cent w/w of HNO3 and about 16 M in strength.
DESCRIPTION Corrosive, fuming liquid.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.42 g (Appendix 4.9).
When solutions of molarity xM are required, they should be prepared by diluting 63x of nitric acid with water to 1000 mL.
Store protected from light.
Nitric Acid, Dilute, Heavy Metal-Free
Use a suitable reagent grade of commerce. Complies with the requirements prescribed
for hydrochloric acid with the following maximum contents of heavy metals in ppm:
Arsenic 0.005, Cadmium 0.005, Copper 0.001, Iron 0.02, Mercury 0.002, Nickel 0.005,
Lead 0.001, and Zinc 0.01.
Nitric Acid, Fuming HNO3 = 63.01
Contains not less than 95.0 per cent w/w of HNO3.
DESCRIPTION Clear, almost colourless to yellow, fuming liquid.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.5 g (Appendix 4.9).
CHLORIDE Not more than 50 ppm (Appendix 5.2). A 5.0-mL portion shows no more chloride than that corresponds to 0.50 mL of 0.020 M hydrochloric acid.
IRON Not more than 1 ppm. Evaporate 7.0 mL on a water-bath to dryness, add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid and dilute to 50 mL with water. The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Iron” (Appendix 5.2).
SULFATE Not more than 0.16 per cent w/w (Appendix 5.2). Dilute 0.20 mL with 5 mL of water,add 10 mg of sodium hydrogencarbonate, and evaporate to dryness on a water-bath. The residue shows no more sulfate than that corresponds to 0.50 mL of 0.010 M sulfuric acid.
SULFATED ASH Not more than 0.01 per cent w/w (Appendix 5.3).
ASSAY Weigh accurately about 2 g into a stoppered flask containing 40ml of water, and titrate with 1 M sodium hydroxide VS, using methyl orange TS as indicator. Each ml of 1 M sodium hydroxide VS is equivalent to 63.01 mg of HNO3.
Nitric Acid, Heavy Metal-Free
Use a suitable reagent grade of commerce. Complies with the requirements prescribed
for hydrochloric acid with the following maximum contents of heavy metals in ppm:
Arsenic 0.005, Cadmium 0.005, Copper 0.001, Iron 0.02, Mercury 0.002, Nickel 0.005,
Lead 0.001, and Zinc 0.01.
Nitrogen N2 = 28.01
Use a laboratory cylinder grade of commerce, washed with water and dried.
Nitrogen for Chromatography Nitrogen containing not less than 99.95 per cent v/v of N2.
Nitrogen, Oxygen-free Nitrogen which has been freed from oxygen by passing through alkaline pyrogallol TS.
Olive Oil
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
FREEZING TEMPERATURE 110° (Appendix 4.4).
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.4680 (Appendix 4.7).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 0.910 g (Appendix 4.9).
Oracet Blue 2R [1-Amino-4-(phenylamino) anthracene-9,10-dione; CI 61110] C20H14N2O2 = 314.34
Use a suitable grade.
Palmatine Iodide C21H22INO4 = 479.31
DESCRIPTION Yellow needles.
SOLUBILITY Sparingly soluble in hot water and ethanol.
Pectolinarigenin C17H14O6 = 314.30
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent.
DESCRIPTION Yellow powder.
SOLUBILITY Sparingly soluble in ethanol and methanol.
Store in tightly closed containers at a temperature not exceeding 25°, protected from light.
Petroleum Ether (Light Petroleum)
| Caution Petroleum Ether is dangerously flammable. Keep away from flames and store in tightly closed containers, in a cool place |
DESCRIPTION Colourless, very volatile,highly flammable liquid,obtained from petroleum,consisting of a mixture of lower members of the paraffin series of hydrocarbons supplied in the following fractions:
boiling range, 30° to 40°; weight per ml, about 0.63 g
boiling range, 40° to 60°; weight per ml, about 0.64 g
boiling range, 50° to 70°; weight per ml, about 0.66 g
boiling range, 60° to 80°; weight per ml, about 0.67 g
boiling range, 80° to 100°; weight per ml, about 0.70 g
boiling range, 100° to 120°; weight per ml, about 0.72 g
boiling range, 120° to 160°; weight per ml, about 0.75 g.
Phosphomolybdic Acid H3PO4·12MoO3·24H2O = 2257.62
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Fine, orange-yellow crystals.
SOLUBILITY Very soluble in water.
Phosphorus Pentoxide Desiccant (Diphosphorus Pentoxide) P2O5 = 141.94
Use a grade specially supplied for use in desiccators.
DESCRIPTION White, amorphous, deliquescent powder hydrated by water with the evolution of heat.
Store in well-closed containers .
Piceatannol C14H12O4 = 244.24
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent.
DESCRIPTION Yellow-tan to brown-pink powder.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in ethanol.
Store in tightly closed containers at a temperature between 2° and 8°.
Piperine C17H19NO3 = 285.34
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C17H19NO3.
Polyethylene Glycol 4000 (Macrogol 4000)
DESCRIPTION White, free-flowing powder or creamy-white flask.
SOLUBILITY Very soluble in water; freely soluble in methanol and in pyridine; practically insoluble in ethanol and in anhydrous ether.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.212 (Appendix 4.9).
MELTING RANGE 54° to 58° (Appendix 4.3).
VISCOSITY At 100°, 76 to 110 mm2.s-1 (Appendix 4.10).
Potassium Hydroxide KOH = 56.11
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION White or practically white,fused masses,or small pellets, or flaskes,or sticks, or other forms.
SOLUBILITY Freely soluble in water, in ethanol and in glycerol; very soluble in boiling ethanol.
Store in tightly closed containers.
Potassium Iodide KI = 166.0
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION White crystalline powder.
Potassium Permanganate KMnO4 = 158.03
Use an analytical grade of commerce.
1-Propanol (n-Propyl Alcohol) C3H8O = 60.10
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid,.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water and with ethanol.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 95 per cent distils between 96° and 99° (Appendix 4.5).
2-Propanol (Isopropanol) C3H8O = 60.10
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid; odour, characteristic.
BOILING RANGE 81° to 83° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 0.785 g (Appendix 4.9).
Pyridine C5H5N = 79.10
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid; odour, characteris tic and unpleasant. Hygroscopic.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 115° (Appendix 4.6).
Store in well-closed containers.
Resorcinol C6H6O2 = 110.10
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C6H6O2.
Rhein C15H8O6 = 284.22
DESCRIPTION Yellow needles.
SOLUBILITY Practically insoluble in water; soluble in alkalis and in pyridine; slightly soluble in benzene, in chloroform, in ethanol, in ether, and in petroleum ether.
MELTING RANGE 321° to 322°, decomposed at 330° (Appendix 4.3).
Rosmarinic Acid C18H16O8 = 360.32
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 percent of C18H16O8.
Ruthenium Red (Ammoniated Ruthenium Oxychloride) C16H42N14O2Ru3 = 786.35
DESCRIPTION Dark brown powder.
SOLUBILITY Completely soluble in water yielding a bright crimson solution; soluble in lead acetate TS.
Rutin C27H30O16 = 610.52
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C27H30O16.
6-Shogaol C17H24O3 = 276.37 Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of C17H24O3.
DESCRIPTION Pale yellow liquid.
Sinapic Acid (Sinapinic Acid) C11H12O5 = 224.21
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
MELTING TEMPERATURE About 202° (Appendix 4.3).
Sinensetin C20H20O7 = 372.37
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
β-sitosterol β-D-glucoside C35H60O6 = 576.85
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 75.0 per cent.
DESCRIPTION White to off-white powder or crystals.
Store in tightly closed containers at a temperature not exceeding 25°
Sodium Acetate C2H3NaO2·3H2O = 136.08
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
Sodium Borohydride (Sodium Tetrahydroborate) NaBH4 = 37.83
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, hygroscopic crystals.
SOLUBILITY Freely soluble in water, soluble in anhydrous ethanol, decomposing at higher
temperature or in the presence of acids or certain metal salts forming borax and hydrogen.
Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool and dry place, protected from light.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (Sodium Lauryl Sulfate) C12H25NaO4S = 288.38
Use a purified grade of commerce containing not less than 99.0 percent w/w of C12H25NaO4S.
DESCRIPTION White, crystalline flaskes.
Sodium Hydrogencarbonate (Sodium Bicarbonate) NaHCO3 = 84.01
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
Sodium Hydroxide NaOH = 40.00
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION White, or practically white,fused masses, in small pellets,in falskes or sticks, and in other forms.
SOLUBILITY Freely soluble in water and in ethanol.
Store in tightly closed containers
Sodium Sulfate (Glauber’s Salt) Na2SO4·10H2O = 322.19
DESCRIPTION Colourless crystals or white granules;odourless. Efflorescent.Melts at 32.5°
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 1.5 parts of water; soluble in glycerol; insoluble in ethanol.
INSOLUBLE MATTER Not more than 0.01 per cent w/w (Appendix 4.13); use 10.0 g.
pH 5.2 to 8.2, in a 5.0 per cent w/v solution in ammonia- and carbon dioxide-free water (Appendix 4.11).
CHLORIDE Not more than 20 ppm (Appendix 5.2). Dissolve 2.1 g in 50.0 mL of water, and filter if necessary. A 25.0-mL portion of the resulting solution shows on more chloride than that corresponds to 0.03 mL of 0.020 M hydrochloric acid.
ARSENIC Not more than 1 ppm (Appendix 5.2); use a mixture of 3.0 g and 35 mL of water as the Test Preparation.
CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, AND TRIVALENT OXIDE PRECIPITATE Not more than 0.02 per cent w/w. Dissolve about 5 g, accurately weighed, in 75 mL of water, filter, and add 7 mL of ammonium oxalate TS, 2 mL of ammonium phosphate TS, and 10 mL of strong ammonia solution. Stir well, and allow to stand overnight. If any precipitate froms,filter,wash with a 25 percent v/v solution of dilute ammonia solution, ignite at 800°±25° to constant weight.
HEAVY METALS Not more than 5 ppm (Appendix 5.2); use 2.0 g. For the Standard Preparation, use lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb).
IRON Not more than 10 ppm. Dissolve 1.0 g in 47 mL of water; add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid.The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Iron” (Appendix 5.2).
NITROGEN COMPOUNDS Not more than 5 ppm. Dissolve 2.0 g in 60 mL of ammonia-free water in a flask connected through a spray trap to a condenser, the end of which dips beneath the surface of 10 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid. Add to the contents of the flask 10 mL of freshly boiled sodium hydroxide TS and 500 mg of aluminium wire in small pieces, and allow to stand for 1 hour. Distil about 35 mL and dilute the distillate with water to 50 mL. Add 2 mL of sodium hydroxide TS, mix, and add 2 mL of alkaline mercuric-potassium iodide TS; the colour produced is not darker than that produced by 0.1 mL of nitrogen standard solution (100 ppm N) when similarly treated.
Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous Na2SO4 = 142.04
DESCRIPTION White, crystalline powder or granules. Hygroscopic.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 6 parts of water, insoluble in ethanol.
ACIDITY OR ALKALINITY Dissolve 4 g in 100 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. The solution requires for neutralization to the green colour of bromothymol blue TS indicative of pH 7 not more than 0.50 mL of either 0.10 M sodium hydroxide or 0.10 M hydrochloric acid.
LOSS ON IGNITION Not more than 0.5 per cent w/w (Appendix 4.16). Weigh accurately about 2 g, and ignite at a low red heat in a tared dish.
CHLORIDE Not more than 0.07 per cent w/w (Appendix 5.2). A 500-mg sample shows no more chloride than that corresponds to 0.50 mL of 0.020 M hydrochloric acid.
IRON Not more than 20 ppm. Dissolve 500 mg in 40 mL of water and 2 mL of hydrochloric acid. The solution complies with the “Limit Test for Iron” (Appendix 5.2).
Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 = 98.07
When no molarity is indicated, use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing about 96 per cent w/w of sulfuric acid and about 18 M in strength.
DESCRIPTION Colourless, oily, corrosive liquid.
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 1.84 g (Appendix 4.9).
When solutions of molarity xM are required, they should be prepared by carefully adding 54x mL of sulfuric acid to an equal volume of water and diluting to 1000 mL with water.
When “sulfuric acid” is followed by a percentage figure,an instruction to add, carefully, sulfuric acid to water to produce the specified percentage v/v (or,if required, w/w) proportion of sulfuric acid is implied.
Sulfuric Acid, Dilute Add 5.5 mL of sulfuric acid to 60 mL of water, allow to cool and add sufficient water to produce 100 mL. It contains 9.8 percent w/v of H2SO4 and about 1 M in strength.
Sulfuric Acid, Ethanolic Solutions of the requisite molarity may be obtained by mixing sulfuric acid with ethanol as directed under Sulfuric Acid.
When “ethanolic sulfuric acid” is followed by a percentage figure,an instruction to use sulfuric acid diluted with ethanol to produce the specified percentage v/v proportion of sulfuric acid is implied. Prepare by cooling separately the required amount to about –5°,carefully adding the acid to the ethanol. Keep the solution as cool as possible and mix gently.
Talc ( Purified Talc)
A native, hydrous magnesium silicate, sometimes containing a small proportion of aluminium silicate.
LOSS ON IGNITION Not more than 5.0 per cent w/w after ignition at a red heat to constant weight (Appendix 4.16).
ACID-SOLUBLE SUBSTANCES Not more than 2.0 per cent w/w. Digest 1 g with 20 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid at 50° for 15 minutes, add water to restore the original volume, mix, and filter. To 10 mL the filtrate add 1 mL of dilute sulfuric acid, evaporate to dryness, and ignite to cons tant weight; the weight of the residue does not exceed 10.0 mg.
n-Tetradecane C14H30 = 198.39
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with ethanol.
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.428 to 1.429 (Appendix 4.7).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 0.76 g (Appendix 4.9).
Tetrahydrofuran (Tetramethylene Oxide) C4H8O = 72.11
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Clear,colourless,flammable liquid.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 66º (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE About 0.89 g (Appendix 4.9).
Do not distil until it complies with the following test.
PEROXIDES Place 8 mL of starch-iodide TS in a groundglass-stoppered cylinder with a capacity of 12 mL and about 1.5 cm in diameter and add sufficient of the substance being examined to fill the cylinder completely,shake vigorously and allow to stand for 30 minutes protected from light. No colour is produced.
Tetrahydrofuran used in spectrophotometry complies with the following additional requirement.
TRANSMITTANCE Not less than 20 per cent at 255 nm, 80 per cent at 270 nm and 98 per cent at 310 nm, determined using water in the reference cell.
Thymol C10H14O = 150.22
DESCRIPTION Colourless, often large crys tals, or a white, crys talline powder.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in about 1000 parts of water, in 1 part of ethanol, in 1 part of chloroform,in 1.5 parts of ether, and in about 2 parts of olive oil.
MELTING RANGE 48° to 51°, when the melted substance is cooled, it remains liquid at a considerably lower temperature (Appendix 4.3).
NON-VOLATILE MATTER Volatilize 2 g on a water-bath and dry at 105° to constant weight. The residue weighs not more than 1 mg.
Store in tightly closed containers, protected from light.
Thymoquinone C10H12O2 = 164.20
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 95.0 per cent of C10H12O2.
Tin(II) Chloride (Stannous Chloride, Tin Chloride Dihydrate) SnCl2·2H2O = 225.65
Use analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless crystals.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid.
Toluene (Methylbenzene) C7H8 = 92.14
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid; odour, characteristic. Flammable.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with water and with ethanol.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 110° (Appendix 4.6).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.865 to 0.870 g (Appendix 4.9).
Trifluoroacetic Acid C2HF3O2 = 114.02
Use a general reagent grade of commerce.
DESCRIPTION Colourless liquid.
SOLUBILITY Miscible with acetone, with benzene, with carbon tetrachloride, with ethanol, with ether, and with hexane.
BOILING TEMPERATURE About 72° (Appendix 4.6).
RELATIVE DENSITY 1.53 (Appendix 4.9).
Store in tightly closed containers.
Ursolic acid C30H48O3 = 456.71
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 98.0 per cent w/w of C30H48O3.
DESCRIPTION White powder.
Vanillin C8H8O3 = 152.15
DESCRIPTION White or cream-coloured crystalline needles or powder; odour, characteris tic of vanilla.
SOLUBILITY Soluble in 100 parts of water; more soluble in boiling water; freely soluble in
ethanol and in fixed and volatile oils; soluble in 20 parts of glycerol and in solutions of the alkali hydroxides.
MELTING RANGE 81° to 83° (Appendix 4.3).
SULFATED ASH Not more than 0.1 per cent w/w (Appendix 5.3).
Water H2O = 18.02
Use Purified Water of the Official Pharmacopoeia.
Water, Carbon Dioxide-free
Water that has been boiled vigorously for a few minutes and protected from the atmosphere
during cooling and storage.
Water, Distilled
Use Purified Water that has been prepared by distillation.
Xylene C8H10 = 106.17
DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid, consisting mainly of m-xylene with smaller proportions of o- and p-xylenes. Flammable.
SOLUBILITY Insoluble in water; miscible with absolute ethanol.
BOILING RANGE Not less than 90 per cent distils between 136° and 140° (Appendix 4.5).
WEIGHT PER MILLILITRE 0.85 to 0.86 g (Appendix 3.4).
SULFUR COMPOUNDS Boil 10 mL with 1 mL of absolute ethanol and 3 mL of potassium plumbite TS for 15 minutes under a reflux condenser, and allow to stand for 5 minutes;the aqueous layer remains colourless.
REACTION WITH SULFURIC ACID Shake 5 mL with 5 mL of sulfuric acid; the xylene remains colourless and the acid may become yellow but not brown.
NON-VOLATILE MATTER When evaporated on a water-bath and dried at 105° to constant weight, leaves not more than 0.01 per cent w/v of residue.
Xylose C5H10O5 = 150.13
For microbiological purposes, use a suitable grade.
Zinc Powder Zn = 65.38
Use an analytical reagent grade of commerce containing not less than 90.0 per cent of Zn.